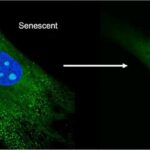
Senolytics are drugs that kill senescent cells. These are cells that have stopped dividing and are no longer able to perform their normal function. Senescent cells have been linked to a number of age-related diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, heart disease, and cancer. There is a growing body of evidence to suggest that senescent cells play a role in the aging process. Senolytic drugs may help to remove these cells and improve the health of older adults. Currently, there are no FDA-approved senolytic drugs. However, there are a few drugs that are being studied for their senolytic effects. These include dasatinib, quercetin, and navitoclax. We are learning about this new field and we hope they will share our site and join on our journey learning about Senolytics.